The color of the sky is something we all see every day, yet the question, Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? remains a curious one for many. People have wondered for centuries why the sky is blue, and this simple question has led to a deeper understanding of light, atmosphere, and physics. By delving into the science behind it, we can finally understand what causes the sky to appear blue, especially during the day.
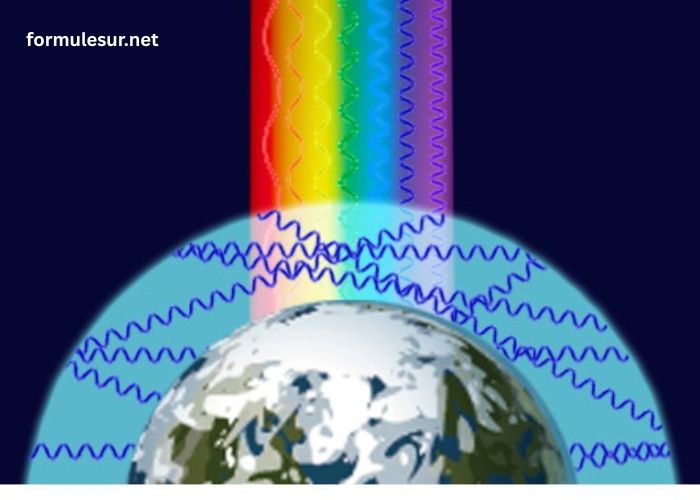
The explanation behind the blueness of the sky lies in the interaction between sunlight and the Earth’s atmosphere. As light from the Sun enters our atmosphere, it is scattered by molecules and small particles. This scattering is not random, but it is selective, which is why we perceive the sky as blue. The science behind this phenomenon is called Rayleigh scattering, a concept that will be explored further as we understand Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? in depth.
What is the Role of Light in Why the Sky is Blue?
The key to answering Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? lies in understanding the behavior of sunlight. Sunlight appears white to the human eye, but it is actually composed of many different colors of light, each with its own wavelength. These colors range from violet to red, with each color having different amounts of energy. The sunlight that reaches Earth consists of all these colors, but the way these colors interact with the atmosphere determines how the sky looks to us.
As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, the shorter wavelengths of light, like blue and violet, are scattered in all directions. This scattering happens because these shorter wavelengths are closer in size to the molecules and particles in the atmosphere. Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? is primarily due to the scattering of blue light, which is why we often associate the color blue with the sky. However, the human eye is more sensitive to blue than violet, which is why the sky appears predominantly blue.
What is Rayleigh Scattering and How Does It Affect the Color of the Sky?
One of the most important concepts in answering Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? is Rayleigh scattering. Named after the British scientist Lord Rayleigh, this phenomenon explains how light is scattered by small particles and molecules in the atmosphere. Rayleigh scattering is most efficient at shorter wavelengths of light, such as violet and blue.
When sunlight enters the atmosphere, it interacts with molecules of nitrogen and oxygen, causing the light to scatter in different directions. Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? can be understood in terms of Rayleigh scattering because the shorter wavelengths, especially blue light, are scattered more than other colors. This scattering causes the blue light to be diffused throughout the sky, making it appear blue to us.
Rayleigh scattering is a process that occurs throughout the day, and its effects are most pronounced when the Sun is high in the sky. As the day progresses and the Sun moves lower in the sky, the light has to pass through a larger portion of the atmosphere, and more scattering of the longer wavelengths, such as red and orange, occurs. This is why we see beautiful sunsets, as the Sun’s rays scatter and filter out the shorter wavelengths, allowing the reds and oranges to dominate.
Why Does the Sky Sometimes Appear Red or Orange?
While Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? is a common question, there are times when the sky appears in different colors, such as red, orange, or even purple. These colors are most commonly observed during sunrise or sunset, when the Sun is near the horizon. At these times, the sunlight has to travel through more of the Earth’s atmosphere, which scatters the shorter wavelengths of light (like blue and violet) and allows the longer wavelengths (like red and orange) to dominate.
The scattering of blue light at sunrise or sunset is much more intense than when the Sun is high in the sky. As a result, the atmosphere’s particles and molecules scatter the shorter wavelengths out of the line of sight, leaving the longer wavelengths, which are red, orange, and yellow, to become more prominent. This is why Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? is most often asked in the context of clear, sunny days, but it is also important to understand the factors that cause the colors to change during different times of the day.
How Does the Presence of Pollution or Dust Affect the Color of the Sky?
The presence of pollution or dust particles in the air can have a significant effect on the color of the sky. Normally, the scattering of light is due to molecules of nitrogen and oxygen, but in polluted areas or during dust storms, there are more particles in the atmosphere that can further scatter light. This changes the way sunlight is filtered, affecting the color of the sky.
When Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? is discussed, it is important to consider that in areas with heavy pollution, the scattering of shorter wavelengths can be altered. Instead of just scattering blue light, the additional particles may scatter a wider range of wavelengths. This can cause the sky to appear more white or hazy rather than the vibrant blue seen on clear days. In some cases, pollution can even cause the sky to take on an orange or brownish hue, especially during sunrise and sunset, when the Sun’s rays pass through more of the atmosphere.
Does the Weather or Time of Day Affect the Blue Color of the Sky?
Weather conditions play a major role in answering the question Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu?. On a clear day, the sky appears blue because the Sun’s rays pass through the atmosphere without much interference, and the short blue wavelengths are scattered. However, weather conditions such as clouds, rain, or snow can block the Sun’s rays and diffuse the light, altering the appearance of the sky.
During cloudy or overcast days, the clouds in the sky scatter the light in all directions, which leads to a dimmer, grayer sky. This is because the clouds act as a barrier to direct sunlight, diffusing the light so that the scattered blue wavelengths are not as prominent. Similarly, when there is heavy rainfall, the sky often appears darker or even almost black, as the water droplets in the atmosphere scatter light differently than the smaller molecules responsible for Rayleigh scattering.
At night, the sky is no longer blue because the Sun is no longer illuminating the atmosphere. The sky becomes dark, allowing us to see the stars and the moon. During this time, the absence of sunlight means there is no light being scattered by the atmosphere, so the sky appears black instead of blue. The time of day, therefore, has a direct influence on the color of the sky, as Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu? is primarily dependent on the presence of sunlight and how it interacts with the Earth’s atmosphere.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the reason why the sky appears blue, Pourquoi Le Ciel Est-Il Bleu?, is due to the scattering of light by the molecules in the Earth’s atmosphere. Rayleigh scattering causes shorter wavelengths, particularly blue light, to scatter in all directions, making the sky appear blue to our eyes.
This phenomenon is influenced by various factors such as the Sun’s position in the sky, the weather, and the presence of particles or pollution in the atmosphere. Understanding the science behind the blue sky not only answers an age-old question but also provides insight into the beautiful, ever-changing colors we see above us every day.